crossed legged tailor position “Buddha” position in Caudal regression syndrome
Caudal regression syndrome represents a spectrum of structural defects of the caudal region. Malformations vary from isolated partial agenesis of the coccyx to lumbosacral agenesis.
Epidemiology
Caudal regression syndrome is rare, with an estimated incidence of 1:7500-100,000 7,10.
The vast majority of cases are sporadic, however, familial cases occasionally occur. An association with VACTERL and Currarino triad syndromic complexes has been reported. Severe cases are usually identified in utero or at birth. Mild cases may not be identified until adulthood. There is no gender predilection.
Associations
congenital genitourinary abnormalities (renal agenesis or hydronephrosis, various forms of duplication of the Mullerian ducts)
anorectal anomalies, particularly anal atresia
other spinal anomalies
vertebral anomalies
diastematomyelia
terminal hydromyelia
myelomeningocele
lipomyelomeningocele
terminal myelocystocele
anterior sacral meningocele
sacral agenesis (sometimes considered as part of the syndrome)
spinal canal lipoma
tethered cord (the cord may be tethered despite being high)
orthopedic abnormalities (range from isolated deformities of the feet (e.g. clubfoot) to lower limb contractures
congenital cardiovascular anomalies
pulmonary hypoplasia
In an antenatal setting there are also associations with:
maternal diabetes: type I or type II
~20% of cases of caudal regression syndrome are associated with either type I or type II diabetes mellitus in the mother
CRS occurs in up to 1% of pregnancies of women with diabetes
Antenatal ultrasound
a blunted sharp ending distal cord on a longitudinal sonogram is typical
the conus often ends way above the expected level (sometimes even higher than L1) 7
absent/hypoplastic sacrum
hypoplastic extended lower extremities (limbs are separated cf. sirenomelia)
may show a “shield sign”: opposed iliac bones in absence of sacral vertebrae: typically seen on an axial scan
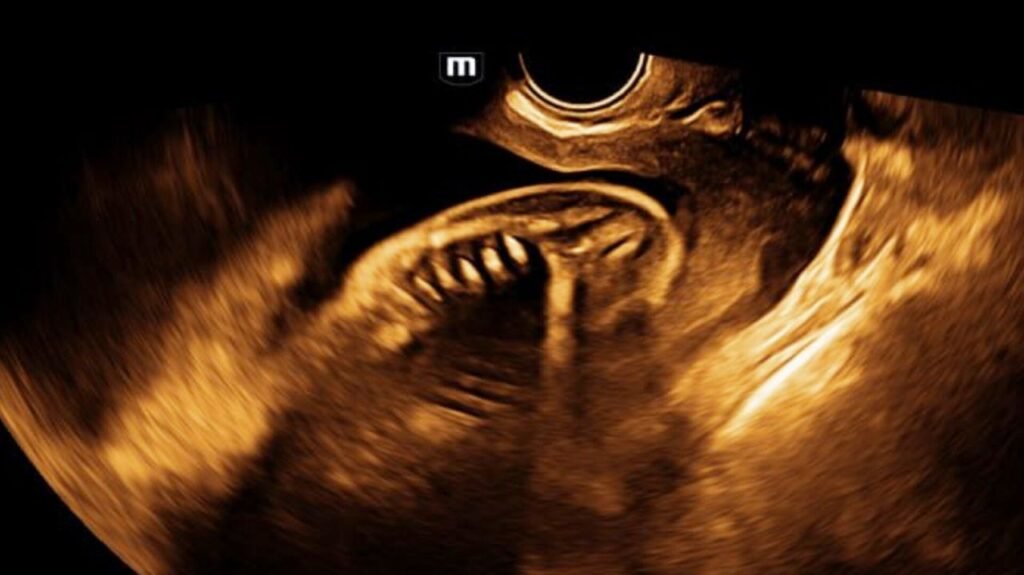
fetal extremities may be seen in a “crossed legged tailor” position or a “Buddha” position
in an early scan (1st trimester), the crown-rump length may be less than expected for gestational age as an indirect feature
polyhydramnios

