Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome fetal ultrasound
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome macroglossia omphalocele +left posterolateral diaphragmatic hernia bochdalek with right mediastinal shift vs Fryn syndrome : micrognathia with protruded tongue & CDH?
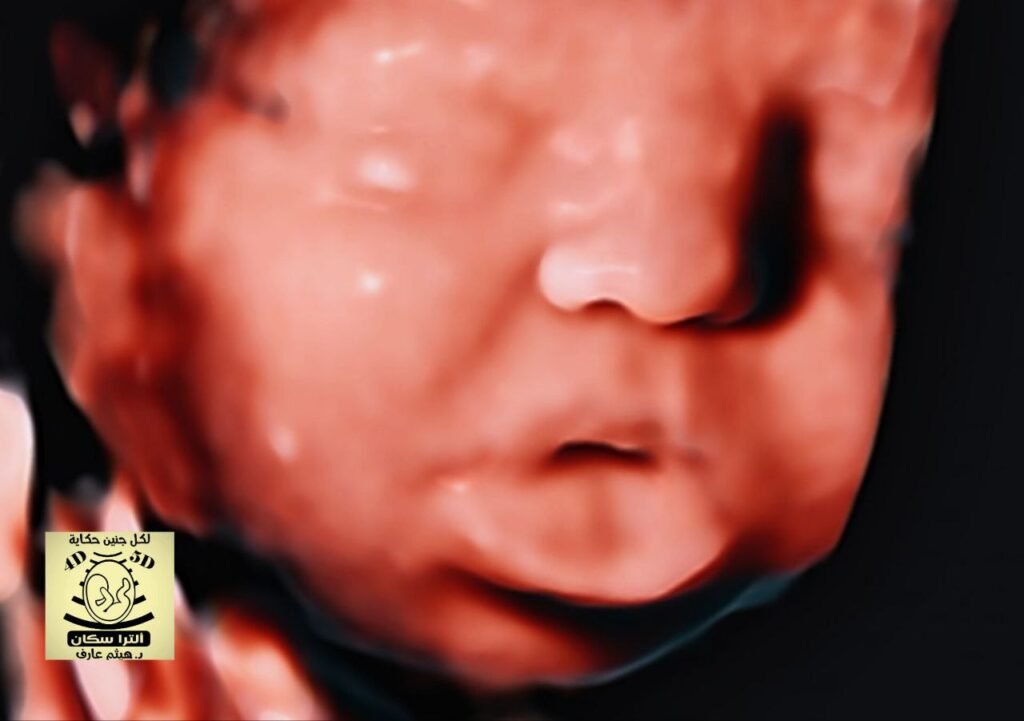
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS), or Beckwith-Wiedemann spectrum, is a congenital overgrowth disorder characterized by a unique set of features that can consist of:
- macroglossia: most common clinical finding
- ear pits or creases
- omphalocele
- localized gigantism / macrosomia
- lateralized overgrowth (hemihypertrophy)
- cardiac anomalies
- pancreatic islet cell hyperplasia
- organomegaly
- nephromegaly
- hepatosplenomegaly
Epidemiology
The incidence is estimated at around 1:10,000 live births. As such, it is the most common overgrowth and cancer predisposition disorder There is no gender or ethnicity predilection.
Associations
- malignancies
- Wilms tumors
- hepatoblastoma
- neuroblastoma
- rhabdomyosarcoma
- adrenocortical carcinoma
- gonadoblastoma
- pancreatoblastoma
- polyhydramnios
- non-malignant renal diseases
- nephromegaly
- renal medullary dysplasia
- calyceal diverticula
- nephrolithiasis in adolescents and adults
- perilobar nephroblastomatosis
- placental pathology
- placentomegaly
- molar degeneration of placenta
- postnatal hypoglycemia
- genitourinary anomalies
- hypospadias
- cryptorchidism
Pathology
The majority of cases are sporadic while a small proportion (5-10%) is autosomal dominant with abnormality related to chromosome 11p15.5 (i.e. Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome critical region). The syndrome carries a well-recognized increased risk for the development of neoplasia ..
History and etymology
First described independently by J B Beckwith in 1963 and H R Wiedemann in 1964 .
Differential diagnosis
The following disorders share features with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome:
- Perlman syndrome: extremely rare; organomegaly,

